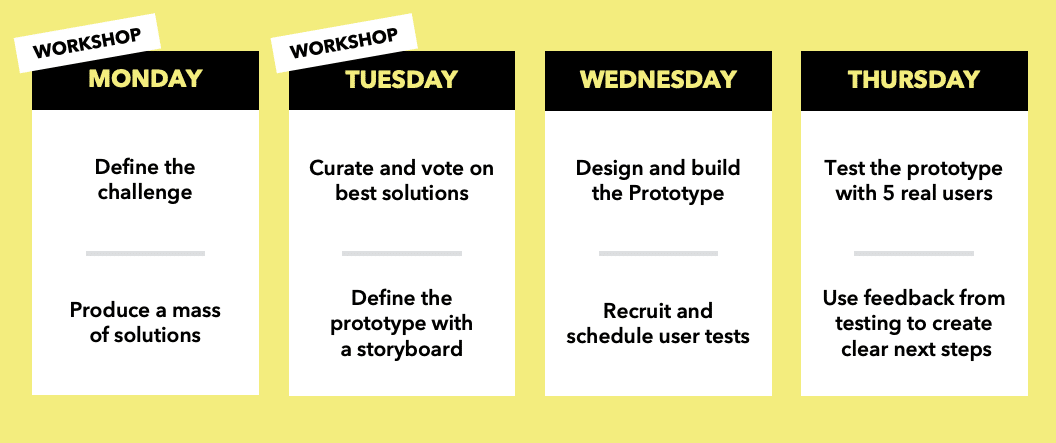
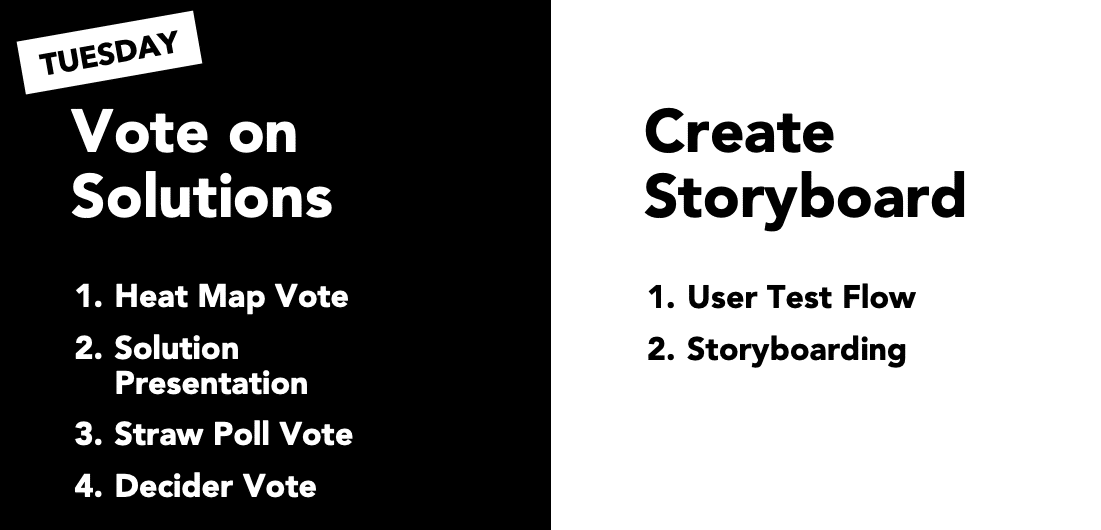
What is a facilitator?
A facilitator is a person who guides and supports a group of individuals in achieving their objectives through the use of facilitation techniques.
The facilitator’s role is to create a favorable environment for communication and collaboration so that the group can work effectively and creatively.
A facilitator can be involved in various types of groups such as work teams discussion groups decision-making groups etc.
The objective of a facilitator is to ensure that the group moves forward effectively and collaboratively to achieve its goals while emphasizing the commitment and participation of each member.
The role of the facilitator is to know how to manage conflicts: It is important to know how to manage conflicts in a way that they do not disrupt the group’s decision-making process.
What kind of training is required to become a facilitator?
However there is no specific mandatory training to become a facilitator.
However it is recommended to receive facilitation training in order to master the techniques and tools needed for this role.
Here are some examples of facilitation trainings:
-
Training in group facilitation
-
Training in meeting facilitation
-
Training in project management
-
Training in leadership
-
Training in conflict management
It is also recommended to become familiar with various facilitation tools and techniques such as brainstorming techniques decision-making techniques problem-solving techniques etc.
In addition to training it is important to have certain qualities and competencies to be a good facilitator such as communication skills active listening empathy flexibility leadership etc. These skills can be acquired through experience and practice in facilitation.
What makes a good facilitator?
Here are some qualities and skills that can make a good facilitator:
Communication: A good facilitator is able to express themselves clearly and concisely so that all participants understand what is being said. They are also attentive to the needs of each participant and know how to adapt their message accordingly.
Active listening: a good facilitator knows how to listen attentively and without prejudice to the ideas and opinions of all participants. They are also able to rephrase ideas in a way that can be understood by everyone.
Empathy: A good facilitator is able to put themselves in the shoes of others and understand their perspectives. They are kind and patient and know how to encourage everyone to speak up and participate.
Flexibility: a good facilitator knows how to adapt to different situations and different groups of people. They are capable of adjusting to different paces and levels of participation.
Leadership: A good facilitator knows how to lead a discussion in a way that remains productive and focused on the established goals. They are capable of making decisions and guiding the group towards creative and viable solutions.
Preparation: a good facilitator is well prepared and does not need to be an expert on the topic they are facilitating. Instead they rely on other members to obtain the information they need.
To summarize, a good facilitator is someone who is able to create a conducive environment for communication and collaboration guide the group towards achieving its objectives in an effective and creative manner and adapt to different situations and groups of people.
It is important to practice and train: practice and training can help you become a better facilitator by giving you the opportunity to apply what you have learned and receive feedback on your work.
Some books on facilitation:
There are numerous books on the topic of facilitation that can help in becoming a very good facilitator.
Here are some titles that might interest you:
-
« The Facilitator’s Fieldbook » from Tom Justice and David W. Jamieson :This book describes the different stages of facilitation and provides practical tools and strategies to assist facilitators in leading effective meetings workshops and decision-making processes.
- « The Skilled Facilitator » from Roger Schwarz : This book offers a holistic approach to facilitation that emphasizes the importance of preparation active listening and conflict management.
- « Facilitator’s Guide to Participatory Decision-Making » from Sam Kaner and al. : This guide provides practical advice on how to establish participatory decision-making processes and create a collaborative working environment.
- « The Art of Facilitation » from Dale Hunter and Anne Bailey : This book presents the fundamentals of facilitation and provides guidance to help facilitators lead effective meetings and workshops.